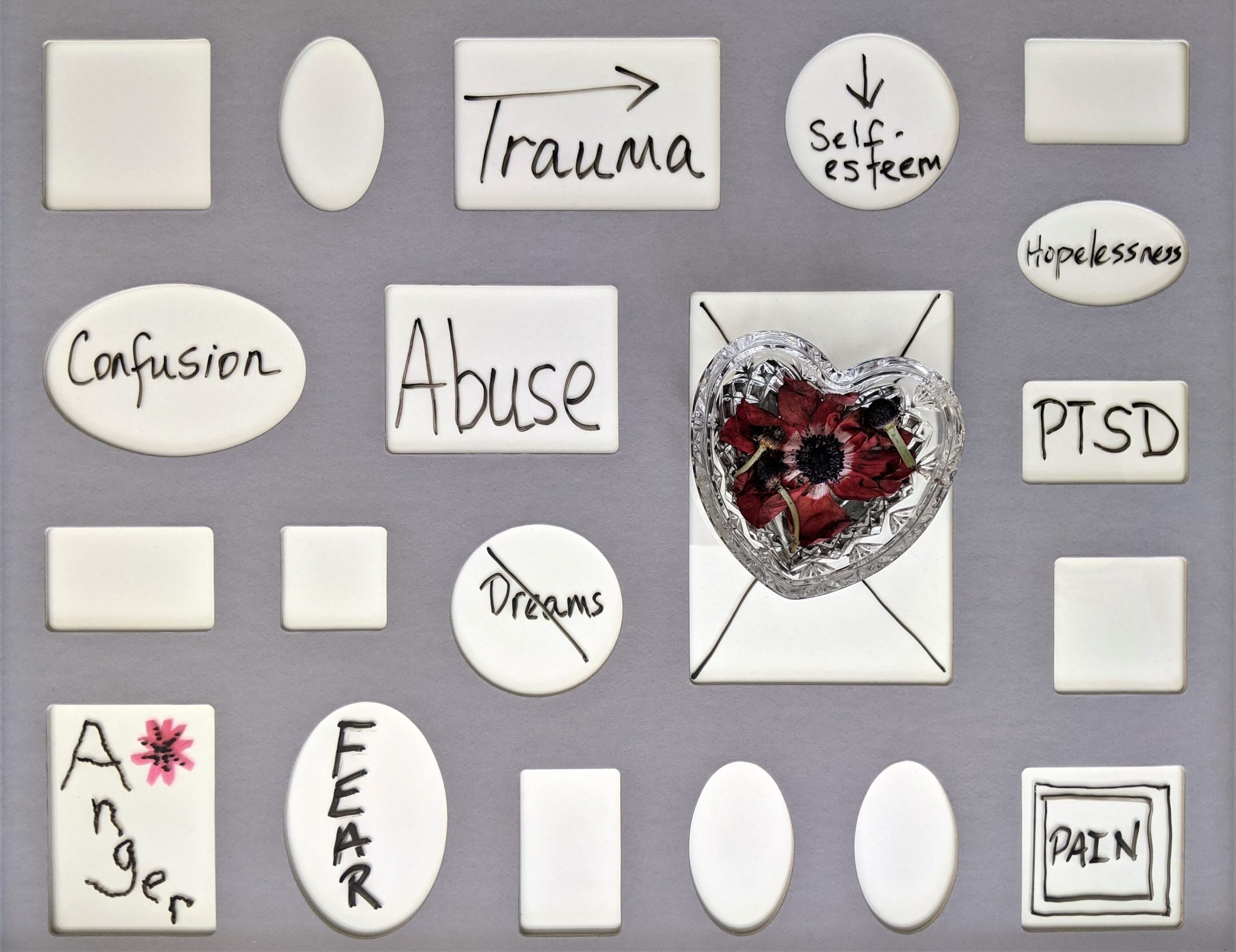
Many of us experienced forms of trauma in our younger years but how does childhood trauma affect adulthood? Here is how it affects us later in life and ways you can treat it.
When we think of childhood thoughts of innocence, optimism and curiosity emerge. Childhood is meant to be a time of security and protections. However, the reality is that most children have experiences that effect the rest of their lives.
As children are brains and bodies are at there most malleable. This means that all our experiences shape us into who we become as adults. When a child suffers a form of trauma, it carries with them into adulthood. Not only does this affect our ways of thinking and behaving but also our relationships with others.
How Does Childhood Trauma Affect Adulthood?
It is the unfortunate truth that many children experience things that effect them into adulthood and sometimes for the rest of their lives. Trauma affects everyone differently and takes many forms.
What Can Childhood Trauma Look Like?
Here are some examples of what childhood trauma looks like:
- Physical or sexual abuse
- Witnessing domestic violence
- Experiencing intense bullying
- Having a sever illness or surgery that required hospitalization
- Experiencing situations like refugee trauma or natural disasters
- Witnessing traumatic events
Childhood Trauma’s & PTSD
Most children experience a traumatic event at one point in their lives. Most of them are able to snap back into a normal state, but some are much more affected than others.
As adults we process things through our education, socialization and life experiences. However, children have no other point of reference which leads them to blame themselves. Childhood trauma takes away from the stability, sense of self and self-worth. This can stay with the child into adulthood, leading to shame, guilt, fear, anxiety, depression and trust issues.
Adulthood Health Consequences
There are many ways that childhood trauma affects adulthood. It leads to trust issues, instability and even long term health issues. Here are several consequences of childhood trauma.
Long-Term Health
Traumatic events can impact a child’s brain development and can have life long consequences. Childhood trauma increases the risk of:
- Depression & anxiety
- Coronary heart disease
- Asthma
- Diabetes
- Stroke
Attachment Disorders
In childhood, the relationship with a caregiver is crucial to their emotional and physical health. The relationship between parent/guardian and child helps them to trust others, manage emotions and interact with the world. If a child cannot rely on the caregiver, it can lead to struggles with maintaining healthy relationships.
Types of attachment disorders:
- Dismissive – Avoidant Attachment: difficult time depending on people close to you, prefer to be alone.
- Fearful – Avoidant Attachment: conflicting feelings about relationships & intimacy, wanting relationships but fearing abandonment, fear of not being good enough for the relationship you want.
- Anxious – Preoccupied Attachment: feelings of needing to feel wanted, jealousy, idolizing romantic partners, need for frequent reassurance.
Unhealthy attachment styles can lead to failed marriages and relationships. It can even have affects on job performance and how you interact with other people around you.
Addiction & Mental Health
Childhood traumas affect on adulthood is linked to addiction and mental health disorders. There is a strong connection between substance abuse, anxiety, depression and eating disorders in adulthood.
People who suffered from trauma as children and did not receive help are more likely to struggle with conflict resolution and have poor stress management abilities as adults. Due to this, many of these individuals may use drugs, alcohol or food as coping mechanisms.
Unhealthy Relationships
Just like attachment disorders, childhood trauma affect on adulthood can lead to being attracted to toxic relationships or unhealthy people. People with past trauma may use it to define their identity, even subconsciously. This means they stay with unhealthy people or situations in order to repeat the cycle of trauma.
Additionally, unhealthy relationships and situations can become addicting in themselves. These individuals are aware of their past and know what they need but still choose to be with people who lead them to a dark path. These traumatic feelings are familiar, which is why many will stay in abusive relationships.
Loss Of Childhood Memories
People who have had a traumatic upbringing may not be able to recall large portions of those years. Blocking is a common defense mechanism that happens when someone does not recognize or can’t accept the past. The reality may be to painful and our brains blocked out the memories in a way to protect us.
Additionally, they may remember vivid memories but without any context. This can lead to issues with self-identity as an adulthood. The loss of memories from childhood can also lead to poor self-esteem and confidence problems.
How To Treat Childhood Trauma In Adulthood
Childhood trauma can have lasting effects on almost every aspect of adulthood. Some without even realizing it. It is never to late to seek treatment or help. Here are some ways that can help treat childhood trauma as adults:
- Acknowledge and recognize the trauma (what it is, who it is, how it affects you everyday)
- Reclaim control (no longer a victim but a survivor)
- Seek support (therapy, groups, trusted friends/family, maintain relationships)
- Take care of your health (exercise, nutrition, daily routine)
- Practice forgiveness, gratitude and mindfulness
- Curb bad habits (smoking, drinking, drugs, nail biting etc.)
- Be patient and stay solution oriented

Bottom Line
A lot of us have trauma from childhood that we may not even be aware of. Our brains may block out painful memories as a defense mechanism. This can also lead to poor self-image and confidence issues. Not only does memory blocking affect us but remembering the trauma can lead to even more issues.
It’s not uncommon for people with trauma from childhood to develop addictions, stay in unhealthy relationships and develop attachment disorders. It is important to remember that you are not alone and there is help out there for you.
Look into local support groups if private therapy is not an option. Learn how to write effective journal entries in order to process and reflect. Take care of yourself and keep working on your mental health!
Follow Us On Instagram!
Stay Connected